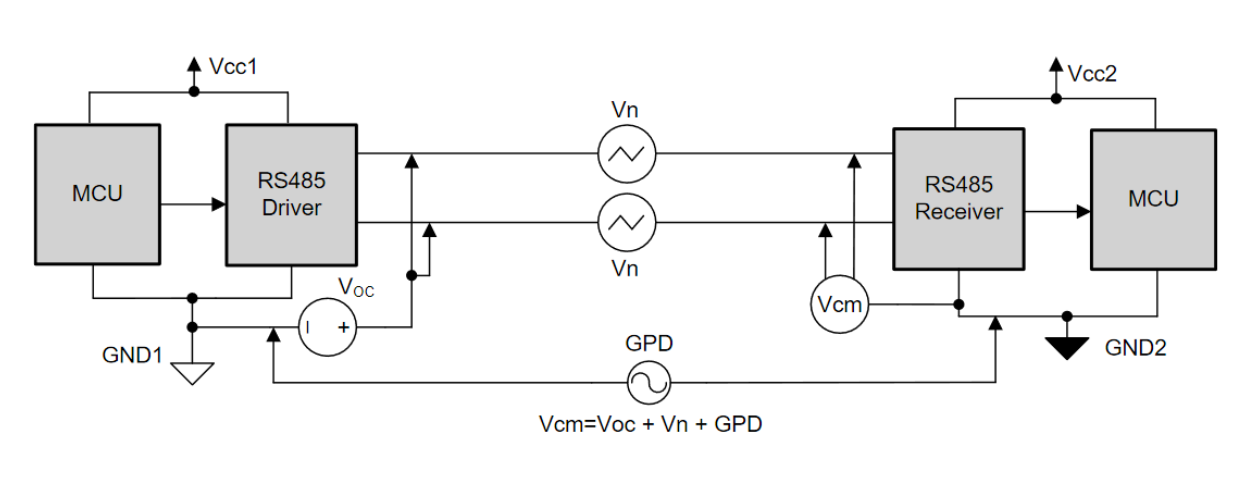
Galvanic isolation for the RS-485port.
RS-485 has been the industry’s most used wired communications interface for more than decades. Balanced differential signaling of RS-485 allows for rejection of common mode noise and facilitates communications over long distances in noisy industrial environments. RS-485 is a common communications port in most industrial applications such as factory automation, protection relay, energy meter, motor drives and building automation.
TIA/EIA-485-A standard defines that the compliant transceivers must work with ±7 V ground potential difference (GPD). As shown in Figure 1, common mode voltage on receiver bus pins (Vcm) is a sum of GPD, driver output common mode voltage (Voc) and any common mode coupled noise (Vn) to the bus pins. As the communication distance between the nodes increases leading to higher GPD or as the industrial environment becomes noisier thereby coupling more common mode noise on the bus, the common mode voltage on receiver bus pins moves out of its recommended operating condition. This can lead to data corruption or damage to the transceiver.
How to isolate RS-485 – smaller size and high reliability – [PDF]