Articles
Categories
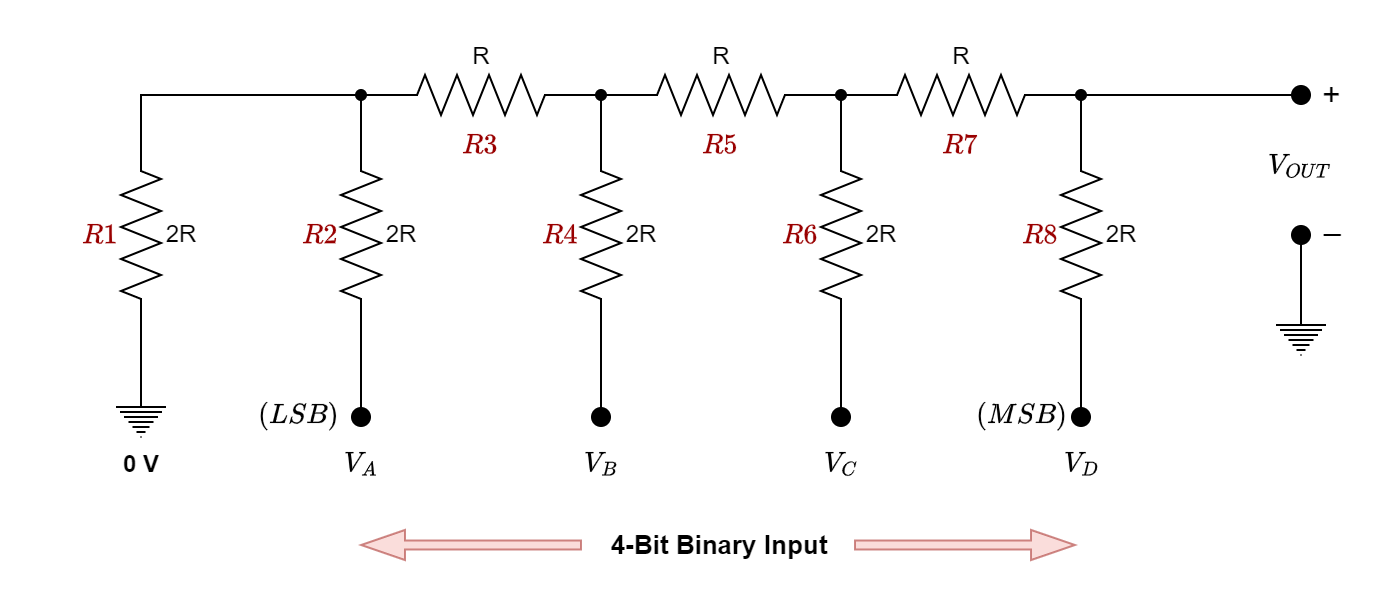
Digital to Analogue Converter (R-2R)
The R-2R Digital-to-Analogue Converter is a type of data converter that transforms a digital binary number into an analog output signal that is proportionate to the...
The R-2R Digital-to-Analogue Converter is a type of data converter that transforms a digital binary number into an analog output signal that is proportionate to the value of the digital number using two precision resistors. The binary-weighted digital-to-analog converter, in contrast to the R-2R DAC, produces an analog output voltage that is the weighted sum […]
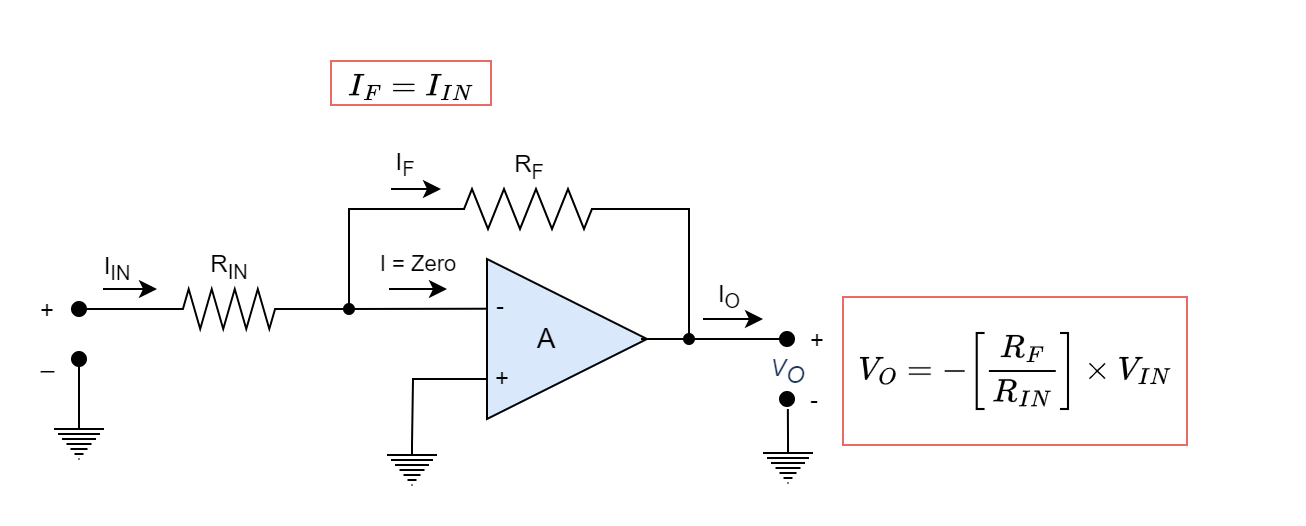
Digital to Analogue Converter (DAC)
Digital-to-Analogue Converter (Binary Weighted) The Digital-to-Analogue Converter (DAC) are opposite of the...
Digital-to-Analogue Converter (Binary Weighted) The Digital-to-Analogue Converter (DAC) are opposite of the Analogue-to-Digital Converter. It employs a method by which binary digital signals are transformed into analogue signals. With its output (voltage or current) proportionate to the value of its digital input number, DACs transform binary or non-binary numbers and codes into analogue ones. Conversion […]
Analog to Digital Converter (ADC)
Analog to Digital Converter An analog-to-digital converter (ADC) is an electronic circuit that is used to convert...
Analog to Digital Converter An analog-to-digital converter (ADC) is an electronic circuit that is used to convert a real-world signal into a digital or binary code. Real-world signals are usually taken from a sensory system which are generally analog in nature and represent instantaneous value of the measured entity. The sensory system may represent any […]
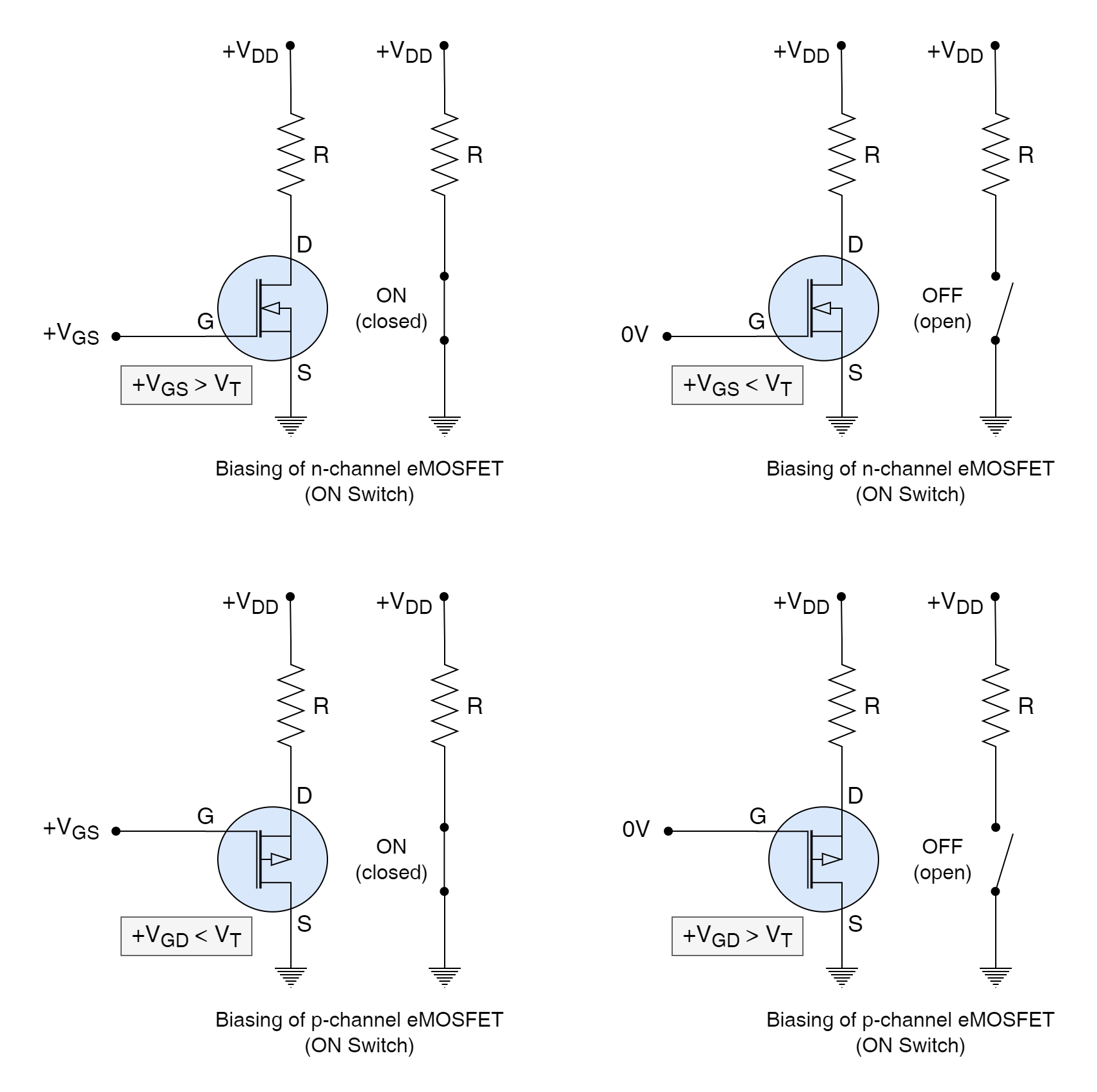
Transmission Gate
Transmission Gate A transmission gate is a form of a bilateral switch constructed using Metal Oxide Field Effect...
Transmission Gate A transmission gate is a form of a bilateral switch constructed using Metal Oxide Field Effect Transistors (MOSFETs) that can be externally controlled through logic levels. A switch, analog one to be precise, controls the passage of analog signals through it and is a type of solid-state semiconductor device. The control of these […]
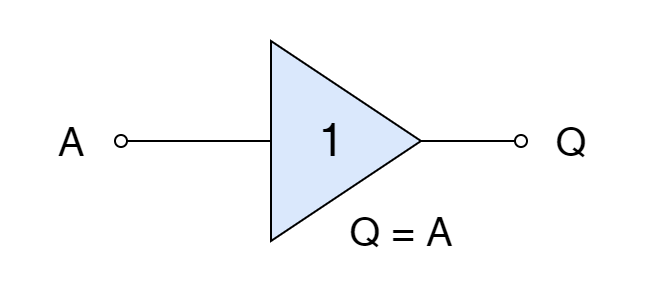
Bus Transceiver
Bus Transceiver A Transceiver is a device allowing a bidirectional interface between buses for either digital or...
Bus Transceiver A Transceiver is a device allowing a bidirectional interface between buses for either digital or analog signal communication and has input & output control capability. It uses back-to-back Tri-state buffers for the communication of multiple devices over a common data bus. Contrary to a Digital Buffer, a Tri-state Buffer allows bidirectional communication and […]
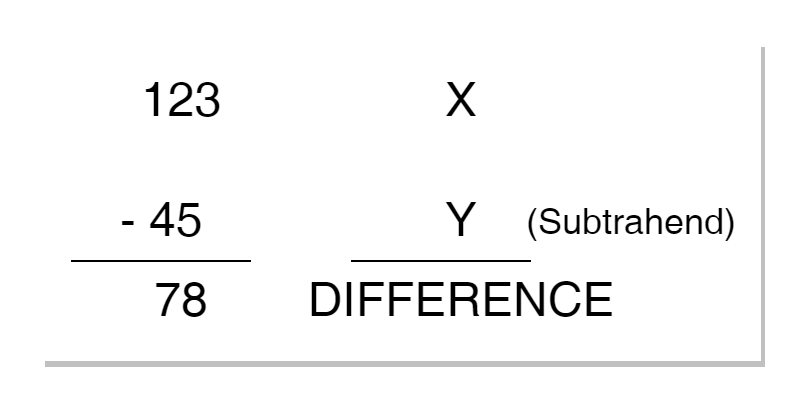
Binary Subtractor
Binary Subtractor The Binary Subtractor is a combinational logic circuit that performs an arithmetic operation of...
Binary Subtractor The Binary Subtractor is a combinational logic circuit that performs an arithmetic operation of subtraction on binary numbers. The output of a Binary Subtractor is the difference (X – Y) resulting from subtracting the two binary inputs (X & Y). It is one of the important arithmetic combinational logic circuits just like Binary […]
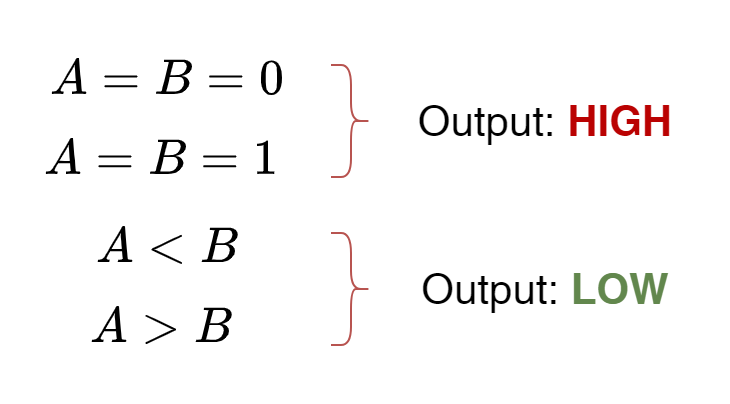
Digital Comparator
Digital Comparator A Digital Comparator is another type of combinational logic circuit that is used to compare...
Digital Comparator A Digital Comparator is another type of combinational logic circuit that is used to compare binary digits. It is a very useful logic circuit used in many digital systems to compare values of digital inputs. A binary comparator can be built using only Standard or Basic logic gates i.e. AND, OR, and NOT […]
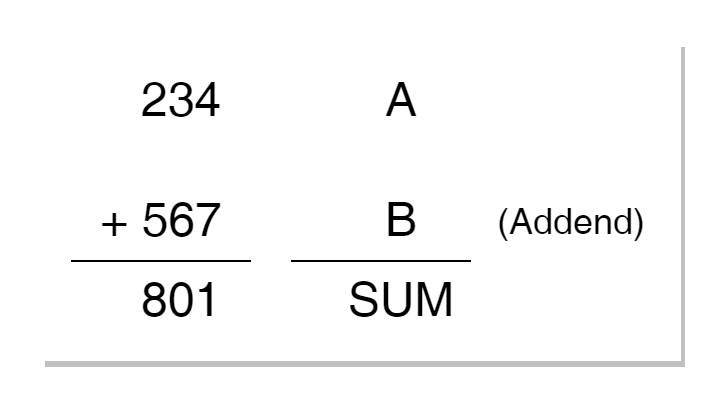
Binary Adder
Binary Adder A digital Binary Adder is a combinational logic circuit that performs the arithmetic operations of...
Binary Adder A digital Binary Adder is a combinational logic circuit that performs the arithmetic operations of addition on binary numbers. The binary adders are usually classified into Binary Half-Adders or Full-adders which perform an arithmetic operation on two binary digits. A simple or basic Binary Adder can be constructed using Exclusive-OR (XOR) and AND […]
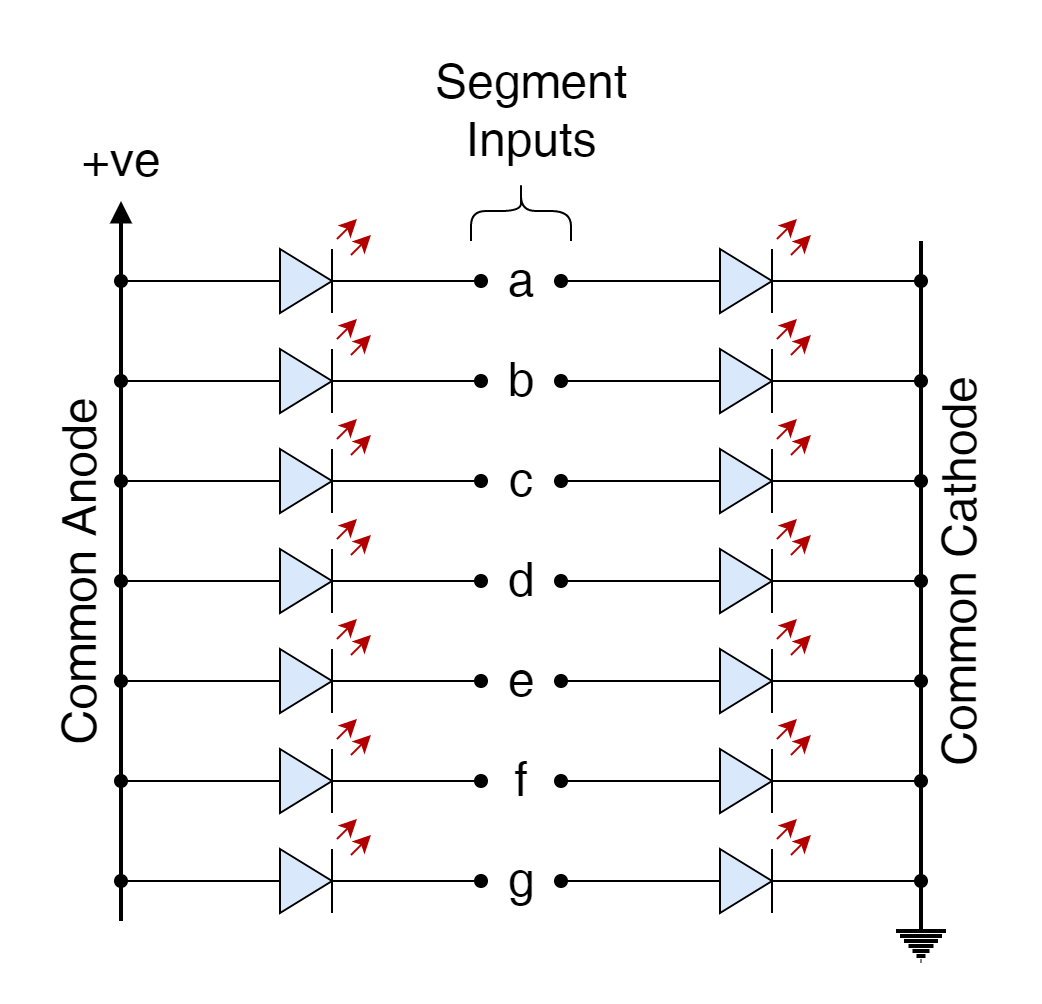
Display Decoder
Display Decoder A Display Decoder is a type of Binary Decoder, discussed in the previous article, with the main...
Display Decoder A Display Decoder is a type of Binary Decoder, discussed in the previous article, with the main purpose to drive a display. As such, it is a combinational logic circuit that converts input binary data into a corresponding number of output lines which are connected to a display for displaying information such as […]
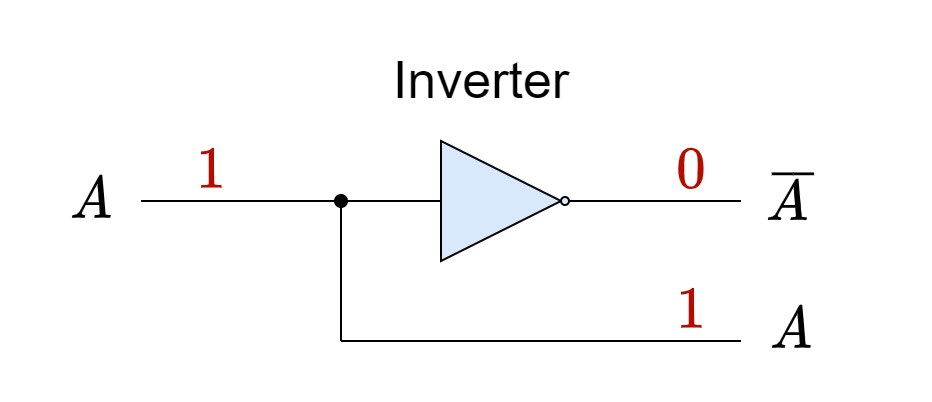
Binary Decoder
Binary Decoder The Binary Decoder is a combinational logic circuit that performs the reverse process of an...
Binary Decoder The Binary Decoder is a combinational logic circuit that performs the reverse process of an Encoder. It produces the original binary input data or signals from the Encoded output signals of an Encoder by decoding them. The “Decoder” term defines a device that translates information from one format into another and, more specifically, […]
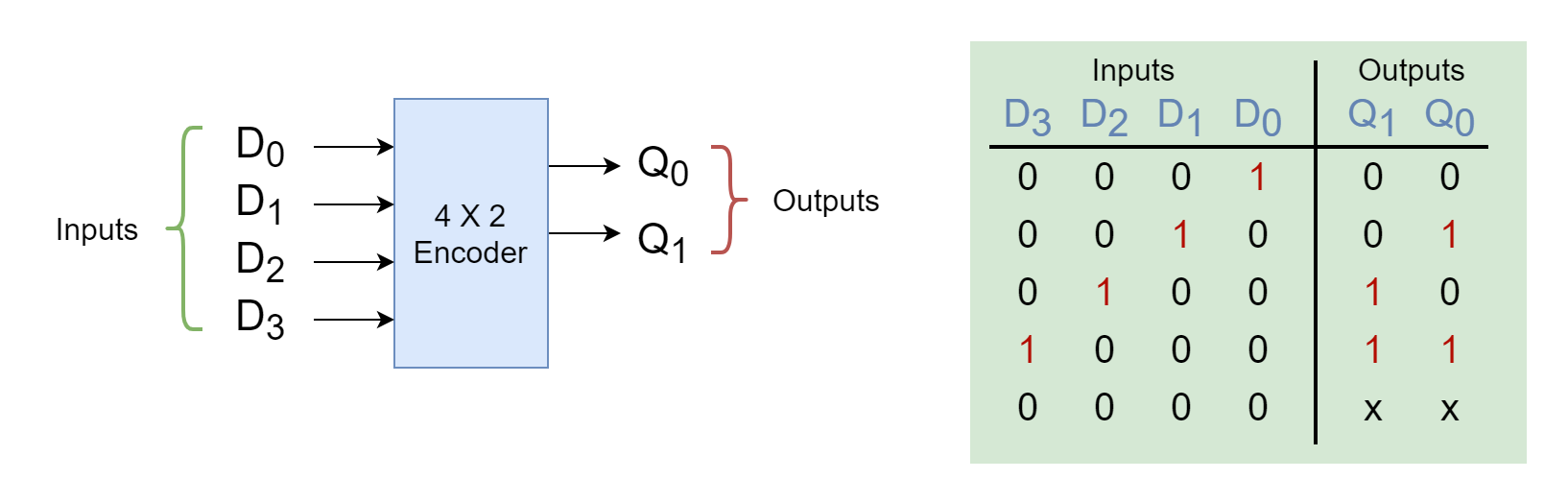
Priority Encoder
Priority Encoder The Priority Encoder is a combinational logic circuit that produces an equivalent binary code at...
Priority Encoder The Priority Encoder is a combinational logic circuit that produces an equivalent binary code at its output pins, unique to each combination state of its inputs. As discussed in previous articles, an encoder produces a unique binary code that is related to a specific input combination, and the inputs handled by an encoder […]
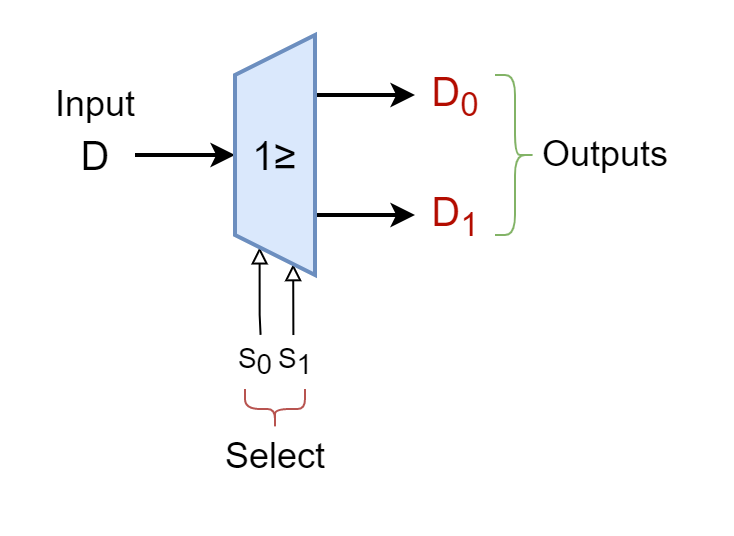
The Demultiplexer
The Demultiplexer The Demultiplexer or DEMUX is a combinational logic circuit that connects one input line to one...
The Demultiplexer The Demultiplexer or DEMUX is a combinational logic circuit that connects one input line to one of the several output lines, one at a time. Like a Multiplexer, the Demultiplexer contains no memory, storage, or feedback. Being a combinational logic circuit, its output is solely dependent on the information present on its input […]
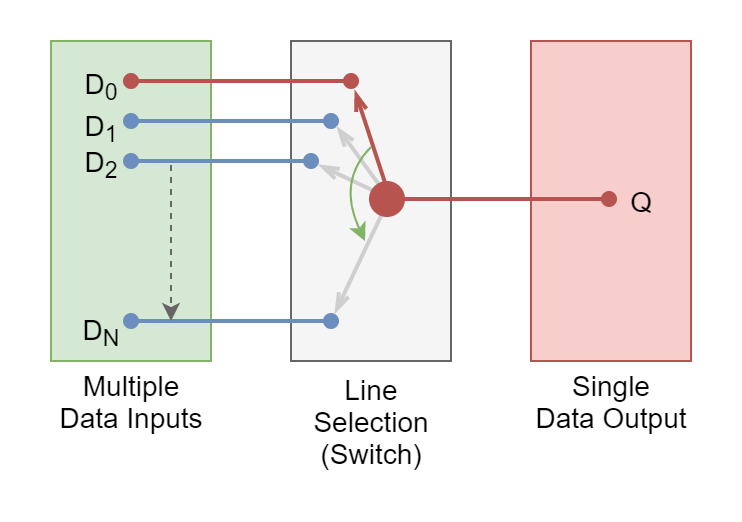
The Multiplexer
The Multiplexer The Multiplexer or MUX is a combinational logic circuit that connects one of the several input...
The Multiplexer The Multiplexer or MUX is a combinational logic circuit that connects one of the several input lines to a single output line. It is a combinational logic circuit and, as such, it is memoryless, without storage, and feedback involved. The multiplexer’s output is solely dependent on the information present on its input lines. […]
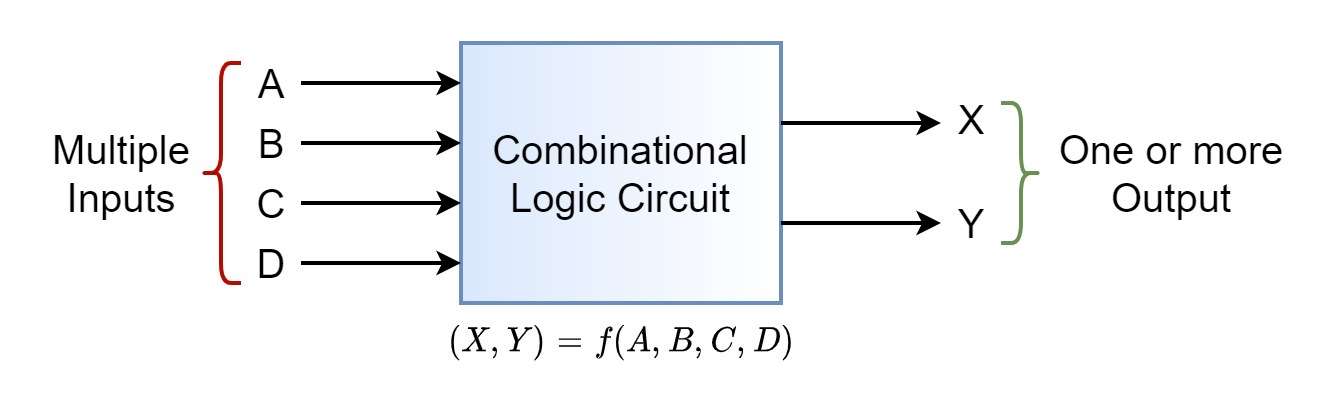
Combinational Logic Circuits
Combinational Logic Circuits The digital logic circuit whose output, at any instant, is dependent on its inputs...
Combinational Logic Circuits The digital logic circuit whose output, at any instant, is dependent on its inputs only is referred to as a combinational logic circuit. The output state(s) of the combinational logic circuit is the logical result of the combination of its inputs and does not involve any kind of memory or storage etc. […]