NGK develops high heat resistance lithium-ion battery achieving an operating temperature of up to 105°C
The new battery is scheduled for mass production in September 2020, with potential applications primarily in automotive and industrial IoT devices.
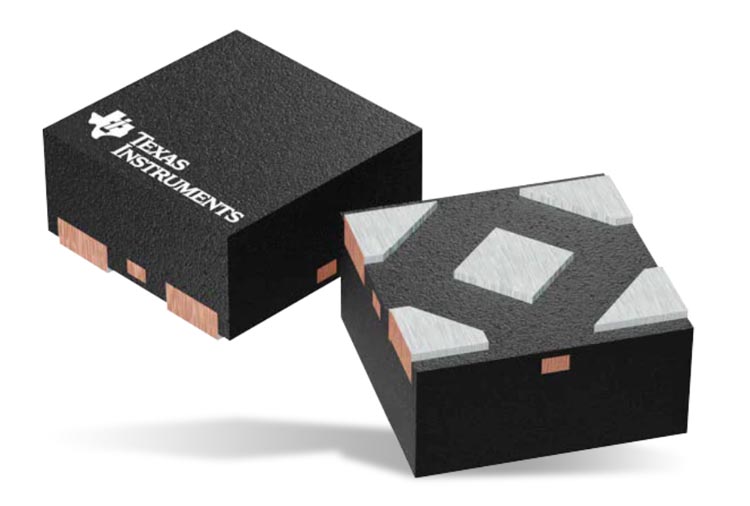
NGK INSULATORS, LTD. (hereinafter “NGK”) has successfully raised the maximum operating temperature of its coin-type “EnerCera Coin” (part of the “EnerCera®” series) battery up to 105 degrees Celsius. Sample shipments are currently underway, with mass production scheduled to begin in September 2020.
In December 2019, NGK developed the world’s first lithium-ion rechargeable battery which has achieved an operating temperature range of -40 to +85 degrees Celsius. As a result of improvements to the product based on customer feedback, NGK recently succeeded in increasing the upper limit of the operating temperature by 20 degrees. The battery is now capable to be used at an operating temperature of up to 105 degrees Celsius, while still maintaining capacity and power. In its fully charged state, when the battery is most prone to deterioration, the capacity decrease is less than 20% even after it is kept at 105 degrees for 1000 hours.
NGK’s EnerCera Coin battery has a unique structure in which a small amount of electrolyte is added to its all-ceramic stacked monolithic body with electrodes and a separator. This provides high thermal stability. The EnerCera battery is categorized as semi-solid-state battery, with performance equivalent to or better than that of a conventional lithium-ion rechargeable battery. The EnerCera battery’s excellent heat resistance characteristics are comparable to those of all-solid-state batteries.
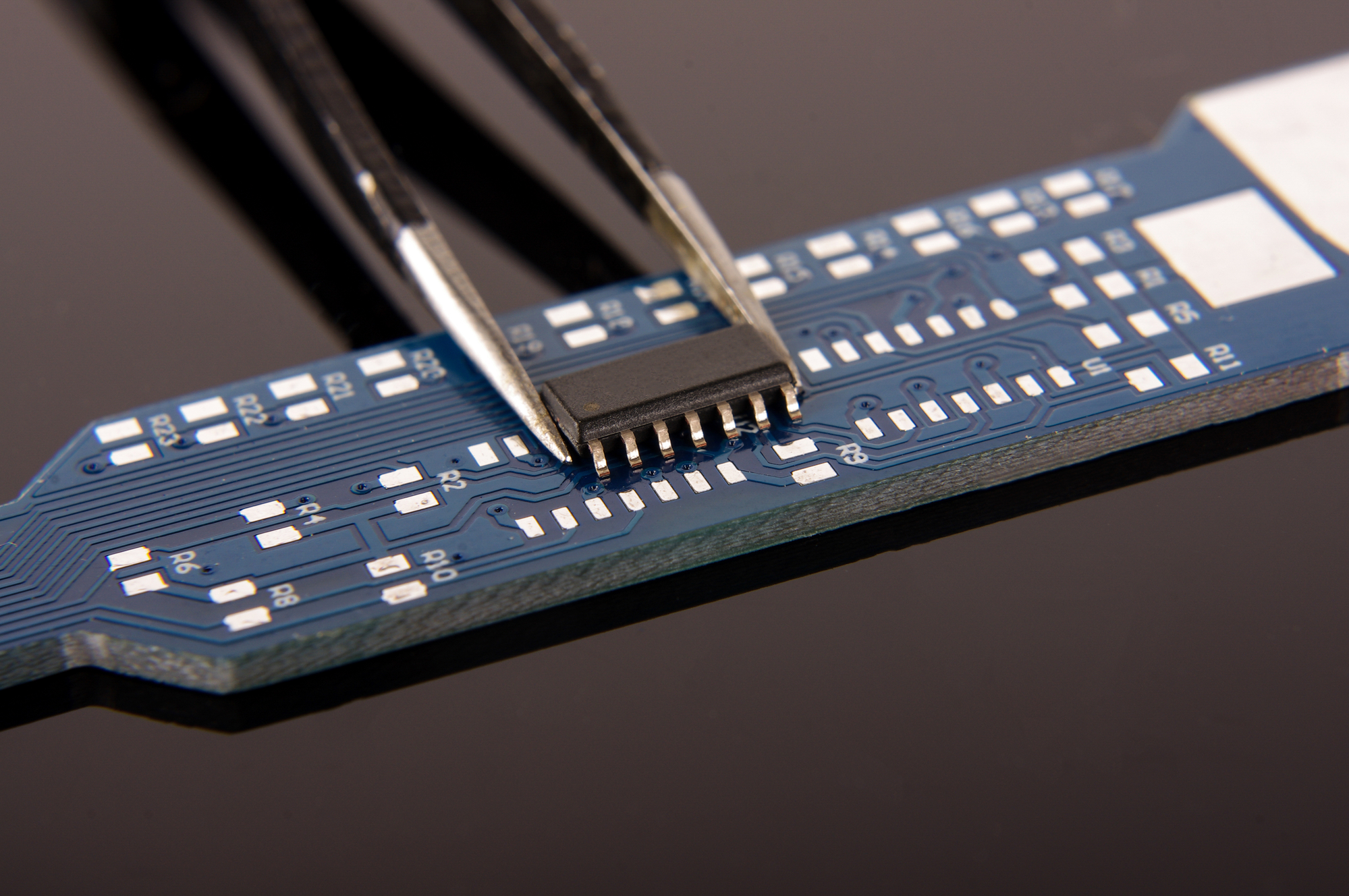
In addition, EnerCera Coin offers flexibility in installation. It can be mounted on a circuit board by reflow soldering, which is a common method for mounting electronic components on board. Furthermore, the battery can also be mounted through injection molding, where molten resin with temperatures of up to 300 degrees is poured into the mold and the battery directly embedded into the resin structure. This allows for the realization of an electronic device with unprecedented design and robustness.
With regard to the latest technological improvements, Iwao Ohwada, Vice President at NGK commented that the:
“development of high heat resistance products was realized through feedback from various partners in the automotive, industrial, logistics and smart card industries. We will continue to work closely with our partners to develop innovative solutions that accelerate the spread of IoT solutions.”
more information: www.ngk-insulators.com