Earlier this month, Google released Android Things 1.0 and announced many consumer products that will ship in the coming months based on the stripped-down, IoT-oriented Android variant. Google uncovered four ARM-based production boards for Android Things 1.0: Innocomm’s i.MX8M based on WB10-AT, Intrinsyc’s Open-Q 212A and Open-Q 624A, based on the Snapdragon 212 and 634, respectively, and the MediaTek MT8516.
The most important news with the first market-ready release of Android Things is that Google is offering free OTA security and patch updates for three years to all targeted devices. However, Google needs a licensing deal to deploy more than 100 commercial systems using the OTA updated long-term version of Android Things, and the OS itself is “managed” and tightly controlled by Google.
The modules share the same small footprints of about a 50 x 50mm. They also focus on audio features that might support integration with the Google Assistant voice agent. The first round of consumer devices using Android Things are smart speakers and automation hubs that integrate Google Assistant.
WB10-AT
InnoComm’s 50 x 50mm WB10-AT COM is almost identical to the WB10 module announced in March. The only difference except for the OS is that the AT version ships with 1GB LPDDR4 instead of 2GB. The WB10-AT includes a 1.5GHz, Cortex-A53 based NXP i.MX8M Quad SoC with a 266MHz Cortex-M4 core. It extends 8GB eMMC, 802.11ac, Bluetooth 4.2, and a GbE controller.
The WB10-AT allows HDMI 2.0 with 4K HDR support, as well as extensive audio I/O enabled by the audio-savvy i.MX8M. Audio specs include 4x SAI, DSD512, and S/PDIF.
Open-Q 212A Development Kit
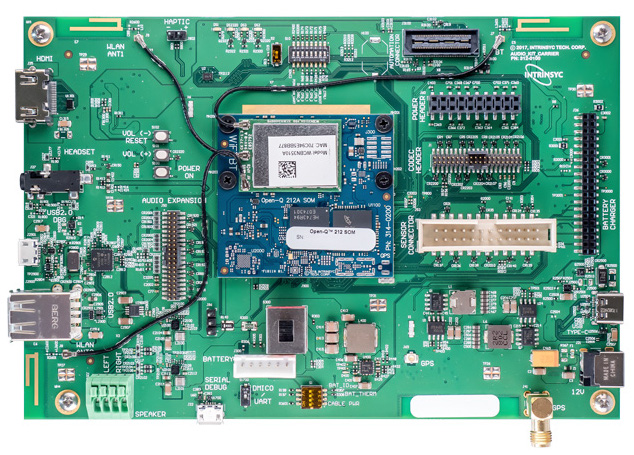
Intrinsyc’s Open-Q 212A is a sandwich-style SBC designed for next-gen smart speaker and voice-controlled home hub products. There is a new 50 x 46.5mm Open-Q 212A Android Things SOM with a quad-core, Cortex-A7 Qualcomm Snapdragon 212 (SDA212) — the lowest-end SoC available for Android Things mounted on a 170 x 115mm carrier board.
The new module provides 1GB LPDDR3, 4GB eMMC, WiFi-ac, and BT 4.2. The 12V carrier board adds 2x USB host ports, a micro-USB client port, and a micro-USB debug port. It also includes a MIPI-CSI and MIPI-DSI interfaces, with the latter capable of up to 720p LCD displays. PCB antennas are also available.
Open-Q 624A Development Kit
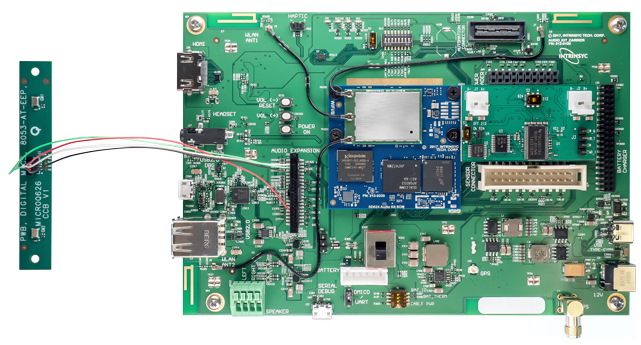
This new sandwich-style kit is Google’s high-end Android Things platform. It connects a new Open-Q 624A Android Things SOM and carrier board, each of which is the same size as their Open-Q 212A counterparts.
The module extends 2GB RAM, 4GB eMMC, WiFi-ac, BT 4.2, and a new, undocumented octa-core Snapdragon 624 SoC based on the existing Snapdragon 625. Like the Snapdragon 625, the 624 provides 8x Cortex-A53 cores at up to 1.8GHz along with an Adreno 506 GPU with support for 4K @ 30fps video. Google calls the Snapdragon 624 the SDA624, and in one place Intrinsyc refers to it as the APQ8053, which is also the name of the Snapdragon 825.
The Open-Q 624A carrier board has a feature set that is very similar to that of the similarly sized Open-Q 212A board. However, it adds a USB 3.0 Type-C port, sensor expansion and haptic output, and an optional GPS receiver, which like the module’s WiFi and Bluetooth, is available with an antenna.
MediaTek MT8516
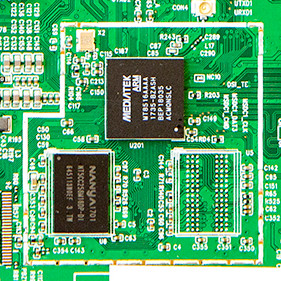
Google refers to the MT8516 as a virtual SoM, as opposed to the other physical modules, and suggests that the module’s capabilities are directly integrated into a reference board designed for high volume applications.
Whatever the form factor, the MT8516 provides a quad-core, 1.3GHz Cortex-A35 processor with 4GB eMMC, WiFi, BT, and RF. The platform is intended for voice assistance and other audio applications and provides 4-channel I2S x2, 8-channel TDM, and 2-channel PDM input for voice input control and connected audio.
The Cortex-A35 cores draw about 33 percent less power per core and occupy 25 percent less silicon area than Cortex-A53. The -A35 design lies at the heart of NXP’s i.MX8X SoC, which is also available in two dual-core models. The i.MX8X is found on Phytec’s phyCore-i.MX 8 module.
More information may be found on this Google Android Things Supported Platforms page, as well as at these four product pages: