Researchers at Samsung in Korea and Stanford University in the US have developed and patented a new architecture for OLED displays with resolution up to 10,000 pixels per inch (PPI). by Nick Flaherty @ eenewsembedded.com
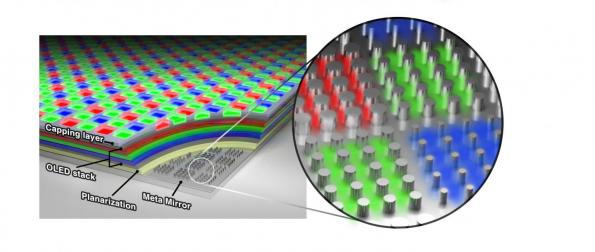
The design uses adapted an electrode ultra-thin solar panels with a base layer of reflective metal with nanoscale corrugations, called an optical metasurface.
The metasurface can manipulate the reflective properties of light and thereby allow the different colours to resonate in the pixels. These resonances are key to improving the light extraction from the OLEDs.
Compared to OLED displays in today smartphones with resolution of 500PPI, the metaphonic pixel array will be able to provide brighter and better colour accuracy for virtual reality displays.
“We’ve taken advantage of the fact that, on the nanoscale, light can flow around objects like water,” said Mark Brongersma, professor of materials science and engineering at Stanford who worked with Won-Jae Joo at the Samsung Advanced Institute of Technology (SAIT). “The field of nanoscale photonics keeps bringing new surprises and now we’re starting to impact real technologies. Our designs worked really well for solar cells and now we have a chance to impact next generation displays,” he said.
The metasonic OLED offers an alternative to the two types of OLED displays that are currently commercially available. Red-green-blue OLEDs have individual sub-pixels that each contain only one colour of emitter. These are fabricated by spraying each layer of materials through a fine metal mesh to control the composition of each pixel. They can only be produced on a small scale.
Larger devices such as TVs use white OLED displays where each of the sub-pixels contains a stack of all three emitters and then relies on filters to determine the final sub-pixel colour. This is easier to fabricate but are more power-hungry as the filters reduce the overall output of light.
In conventional RGB-OLEDs, the different frequencies mean red sub-pixels have a different height from the blue emitters. This means materials deposited above the emitters have to be laid down in unequal thicknesses to create a flat screen. By contrast, the base layer corrugations in the metasonic OLEDs allow each pixel to be the same height for a simpler manufacturing process.
In lab tests, the researchers successfully produced miniature proof-of-concept pixels. Compared with colour-filtered white-OLEDs, the pixels had a higher colour purity and twice the luminescence as well as pixel density of 10,000 per inch.
The next steps for integrating this work into a full-size display is being pursued by Samsung.